Guide to Engines: Difference between revisions
m (→The Radiators) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
=== The Supermatter Crystal (SM) === | === The Supermatter Crystal (SM) === | ||
The supermatter crystal is the source of engineering’s power. It puts out both heat and radiation when energized by lasers, both of which can be turned into electrical energy to power the ship. | The supermatter crystal is the source of engineering’s power. It puts out both heat and radiation when energized by lasers, both of which can be turned into electrical energy to power the ship. As the crystal generates heat, it will pass that heat to the gasses surrounding it in it’s chamber. These gasses are consequently referred to as coolant, regardless of which particular gas you are cooling the SM with. | ||
As the crystal generates heat, it will pass that heat to the gasses surrounding it in it’s chamber. These gasses are consequently referred to as coolant, regardless of which particular gas you are cooling the SM with. | |||
If this heat cannot be moved away from the SM and into the coolant, it will cause the SM to start losing it’s integrity, which will eventually cause delamination. There is a vent in the SM chamber that removes the coolant and pipes it to what is referred to as the hot-loop. | If this heat cannot be moved away from the SM and into the coolant, it will cause the SM to start losing it’s integrity, which will eventually cause delamination. There is a vent in the SM chamber that removes the coolant and pipes it to what is referred to as the hot-loop. | ||
[[File:Sm2.png|thumb|The Thermo-Electric Generator]] | [[File:Sm2.png|thumb|The Thermo-Electric Generator]] | ||
=== The Thermo-Electric Generator (TEG) === | === The Thermo-Electric Generator (TEG) === | ||
The thermo-electric generator takes the heat it receives from the SM’s hot-loop, and uses it to generate electricity by transferring that heat to what is referred to as the cold-loop. | The thermo-electric generator takes the heat it receives from the SM’s hot-loop, and uses it to generate electricity by transferring that heat to what is referred to as the cold-loop. It is the differential of heat between the hot-loop and cold-loop that allows the TEG to generate electricity. As the heat is transferred between the two loops during the process, this effectively cools the hot-loop as well, allowing it to better cool the SM itself. No gas is transferred between the hot and cold pipes, only heat. | ||
It is the differential of heat between the hot-loop and cold-loop that allows the TEG to generate electricity. As the heat is transferred between the two loops during the process, this effectively cools the hot-loop as well, allowing it to better cool the SM itself. No gas is transferred between the hot and cold pipes, only heat. | |||
[[File:Sm4.png|thumb|The Radiators. What lies between you and Delamination]] | [[File:Sm4.png|thumb|The Radiators. What lies between you and Delamination]] | ||
=== The Radiators === | === The Radiators === | ||
The radiators are simply an array of pipes that are passed through the hull of the ship, and out into space, these pipes are particularly thermally conductive, allowing the heat from the pipes to be radiated away into space. This | The radiators are simply an array of pipes that are passed through the hull of the ship, and out into space, these pipes are particularly thermally conductive, allowing the heat from the pipes to be radiated away into space. This process is what keeps the cold-loop coolant colder than the hot-loop, so that it can continue to be used to generate electricity. [[File:Sm3.png|thumb|The Filters]] | ||
=== The Filters === | === The Filters === | ||
Filters are what are used to remove unwanted contaminants from both loops. The SM emits many types of gasses while energized. | Filters are what are used to remove unwanted contaminants from both loops. The SM emits many types of gasses while energized. One of these gases, Oxygen, will react with both hydrogen, and phoron. This creates water, and carbon dioxide respectively. As a result of this, if water and/or carbon dioxide are filtered out from the hot loop, this will result in a gradual, albeit usually safe rate of coolant loss. So be sure to choose your filter settings carefully. | ||
Revision as of 07:11, 28 March 2022
General guide to the power sources of the SGV Dagon.
Guide to the Supermatter
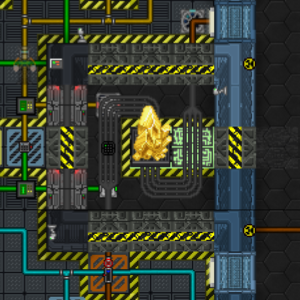
The Supermatter Crystal (SM)
The supermatter crystal is the source of engineering’s power. It puts out both heat and radiation when energized by lasers, both of which can be turned into electrical energy to power the ship. As the crystal generates heat, it will pass that heat to the gasses surrounding it in it’s chamber. These gasses are consequently referred to as coolant, regardless of which particular gas you are cooling the SM with.
If this heat cannot be moved away from the SM and into the coolant, it will cause the SM to start losing it’s integrity, which will eventually cause delamination. There is a vent in the SM chamber that removes the coolant and pipes it to what is referred to as the hot-loop.

The Thermo-Electric Generator (TEG)
The thermo-electric generator takes the heat it receives from the SM’s hot-loop, and uses it to generate electricity by transferring that heat to what is referred to as the cold-loop. It is the differential of heat between the hot-loop and cold-loop that allows the TEG to generate electricity. As the heat is transferred between the two loops during the process, this effectively cools the hot-loop as well, allowing it to better cool the SM itself. No gas is transferred between the hot and cold pipes, only heat.

The Radiators
The radiators are simply an array of pipes that are passed through the hull of the ship, and out into space, these pipes are particularly thermally conductive, allowing the heat from the pipes to be radiated away into space. This process is what keeps the cold-loop coolant colder than the hot-loop, so that it can continue to be used to generate electricity.

The Filters
Filters are what are used to remove unwanted contaminants from both loops. The SM emits many types of gasses while energized. One of these gases, Oxygen, will react with both hydrogen, and phoron. This creates water, and carbon dioxide respectively. As a result of this, if water and/or carbon dioxide are filtered out from the hot loop, this will result in a gradual, albeit usually safe rate of coolant loss. So be sure to choose your filter settings carefully.